mirror of
https://github.com/billbuchanan/appliedcrypto.git
synced 2026-02-21 11:18:02 +00:00
Update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -500,10 +500,25 @@ Run the code and answer the following questions:
|
||||
* Which key (public or private key) is used to verify the signature?
|
||||
* Which key (public or private key) is used to verify the signature?
|
||||
|
||||
# AWS Lab
|
||||
Within digital signatures, we have two main signatures: RSA, ECDSA and EdDSA. In AWS, we can implement RSA (with PSS) and ECDSA.
|
||||
|
||||
## RSA PSS Signatures
|
||||
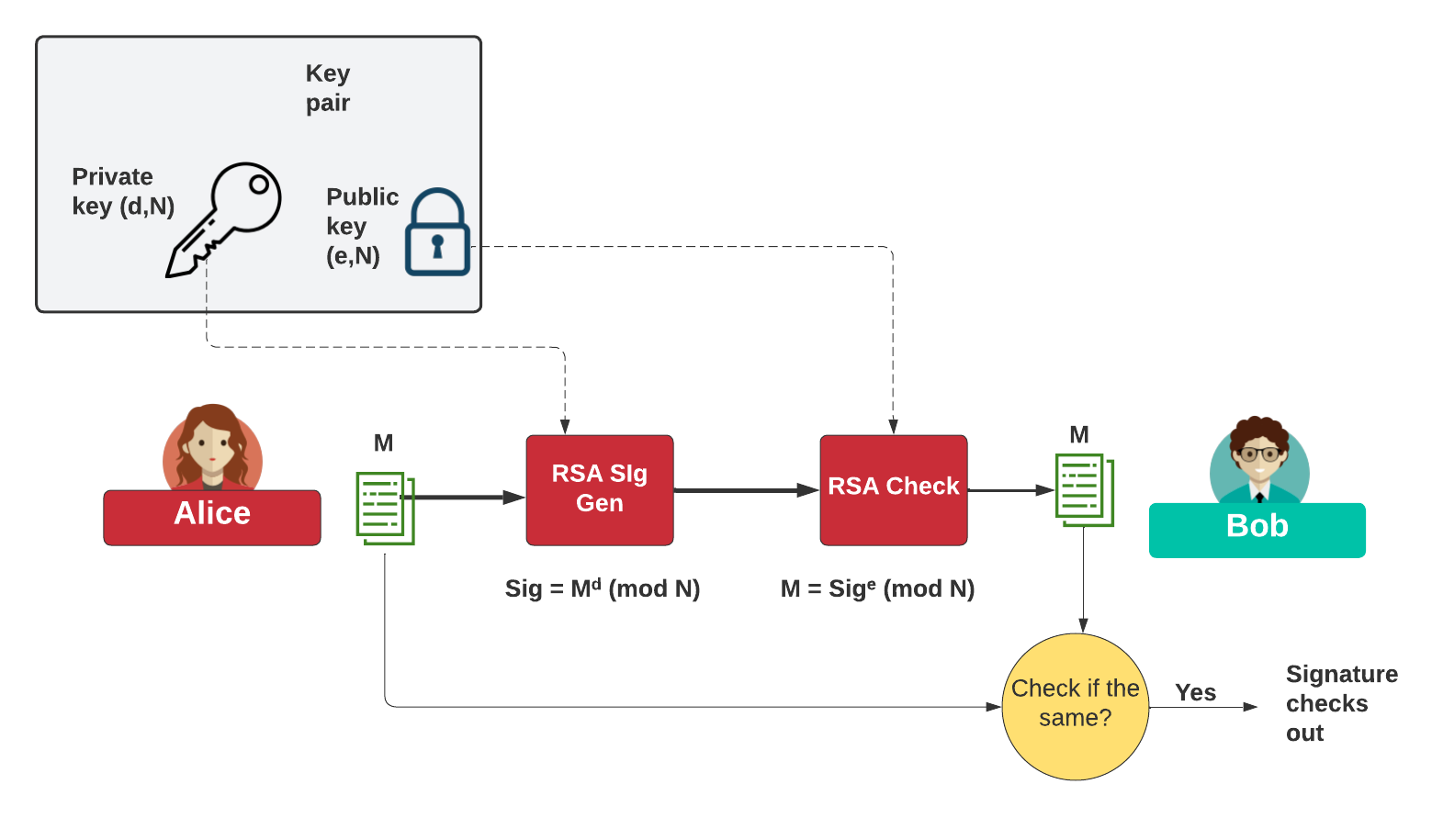
In digital signing, we use our private key to sign for a message, and then the proof of signing is done with our public key. This happens for a Bitcoin transaction, and where we take the private key from our wallet and then sign for a transaction. The public key is then used to prove that the user signing the transaction. While Bitcoin uses ECDSA, we can also use RSA signing. A common method is RSASSA_PSS_SHA_256.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Undertake the lab [here](https://asecuritysite.com/aws/lab09).
|
||||
|
||||
## ECDSA Signatures
|
||||
In digital signing, we use our private key to sign for a message, and then the proof of signing is done with our public key. This happens for a Bitcoin transaction, and where we take the private key from our wallet and then sign for a transaction. The public key is then used to prove that the user signing the transaction.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Undertake the lab [here](https://asecuritysite.com/aws/lab05).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## What I should have learnt from this lab?
|
||||
## What should I have learned from this lab?
|
||||
The key things learnt:
|
||||
|
||||
* Understand how digital certificates are generated and ported onto systems.
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
unit06_trust_dig_cert/lab/~$w_lab06.docx
Normal file
BIN
unit06_trust_dig_cert/lab/~$w_lab06.docx
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
@@ -124,12 +124,12 @@ The following is some sample code you can test your hashes against:
|
||||
import hashlib;
|
||||
import passlib.hash;
|
||||
|
||||
string="password"
|
||||
print "General Hashes"
|
||||
print "MD5:"+hashlib.md5(string).hexdigest()
|
||||
print "SHA1:"+hashlib.sha1(string).hexdigest()
|
||||
print "SHA256:"+hashlib.sha256(string).hexdigest()
|
||||
print "SHA512:"+hashlib.sha512(string).hexdigest()
|
||||
string="password".encode()
|
||||
print ("General Hashes")
|
||||
print ("MD5:"+hashlib.md5(string).hexdigest())
|
||||
print ("SHA1:"+hashlib.sha1(string).hexdigest())
|
||||
print ("SHA256:"+hashlib.sha256(string).hexdigest())
|
||||
print ("SHA512:"+hashlib.sha512(string).hexdigest())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To test your PBKDF2 code, you will have to take the salt generated randomly from your Web page and copy it. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
Binary file not shown.
BIN
unit06a_mini_project/~$b_mini_project.docx
Normal file
BIN
unit06a_mini_project/~$b_mini_project.docx
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
Reference in New Issue
Block a user