mirror of
https://github.com/billbuchanan/appliedcrypto.git
synced 2026-02-21 11:18:02 +00:00
Update README.md
This commit is contained in:
@@ -525,6 +525,99 @@ Now answer the following:
|
||||
* Now send 0.1 of your token to someone else's wallet. If you want, you can send to your tutor's wallet. Bill's wallet is 0xbb15b38e4ef6af154b89a2e57e03cd5cbd752233
|
||||
* Did they receive the token?
|
||||
|
||||
## Saving the state
|
||||
|
||||
Smart contracts give us the opportunity to store data in a stateful way, and where we can add and delete data within the smart contact, and then view a current state. So let’s do a simple contact of adding cities to a string array. Overall it will cost us some gas to add and delete strings, but not to view the state. The contract we will use is:
|
||||
|
||||
```Solidity
|
||||
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
|
||||
|
||||
contract ExampleApp {
|
||||
|
||||
string[] myArray;
|
||||
|
||||
function add(string x) public {
|
||||
myArray.push(x);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
function del(string x) public {
|
||||
for (uint j = 0; j < myArray.length; j++) {
|
||||
if (keccak256(abi.encodePacked(myArray[j])) == keccak256(abi.encodePacked(x))) {
|
||||
|
||||
delete myArray[j];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function show() public view returns (uint256, string) {
|
||||
string memory str;
|
||||
for (uint j = 0; j < myArray.length; j++) {
|
||||
str = string(abi.encodePacked(str, myArray[j]));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return(myArray.length,str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This has an add() method to add a new string to myArray, and a show() which will show the contents of myArray. The view element added to show() makes sure it is just a read function (and that we do not write to the function). We can then compile it in remix:
|
||||
|
||||
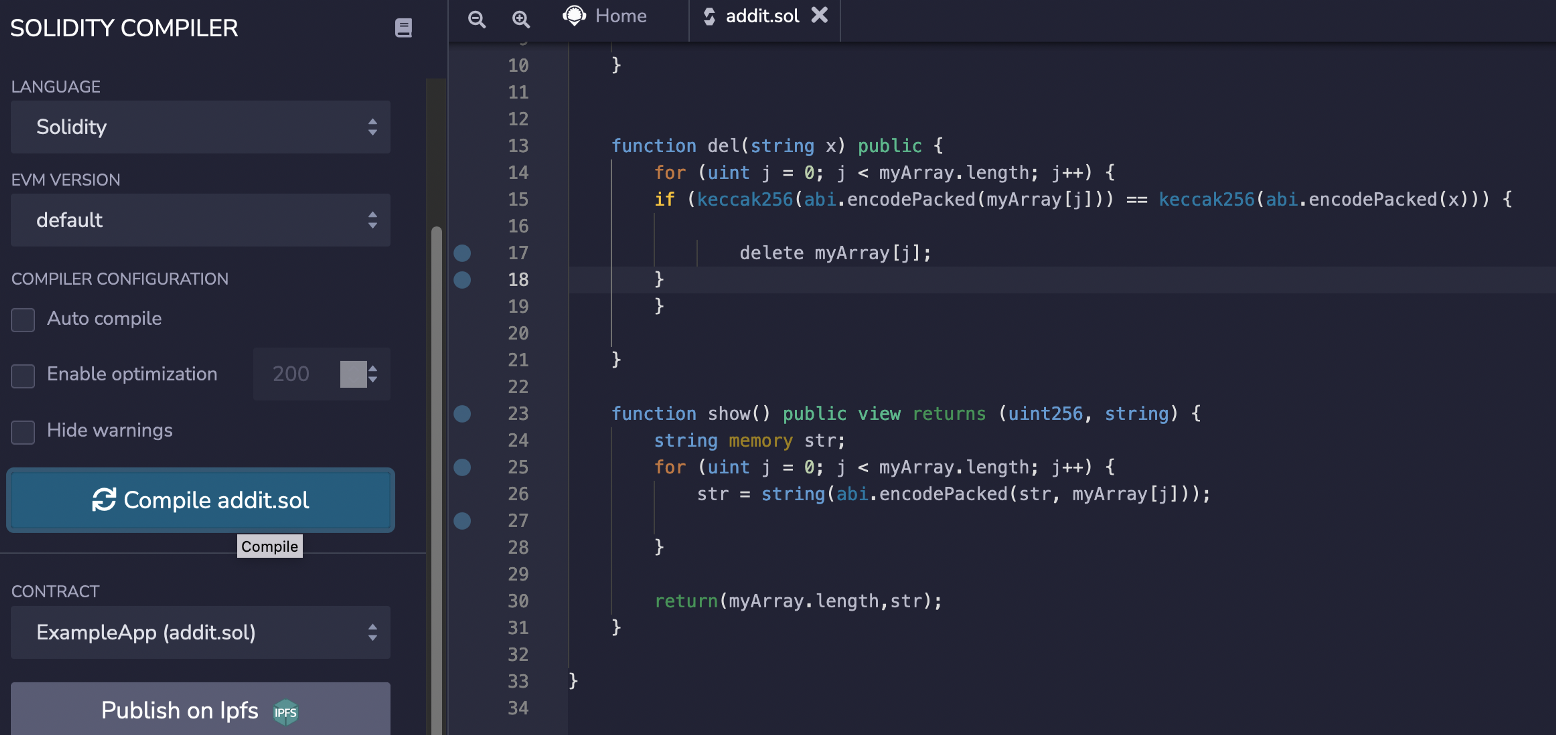
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can deploy:
|
||||
|
||||
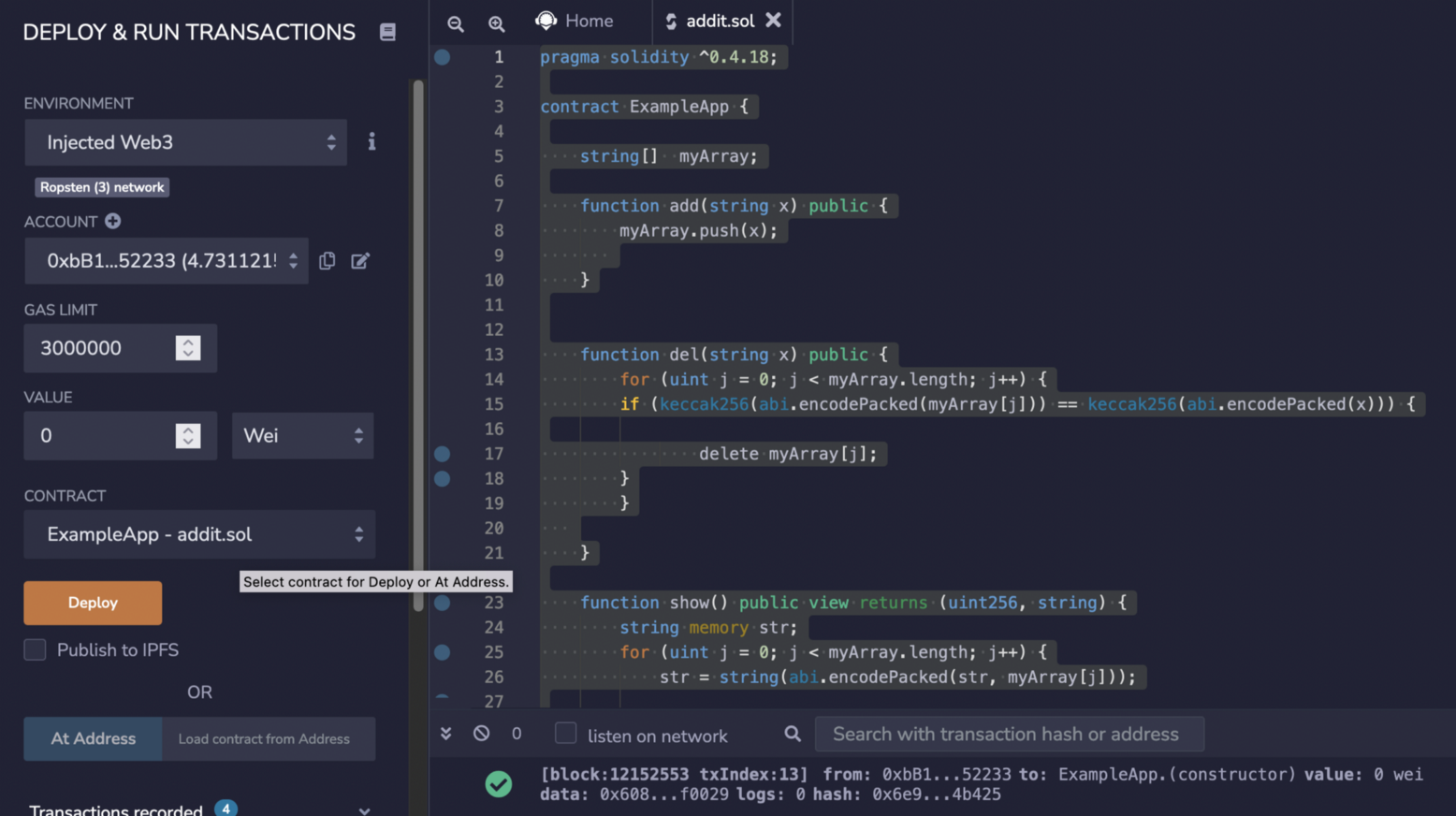
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a new contact [here](https://ropsten.etherscan.io/address/0xc79961ad2fdf3fcb4a57ebeaab78a1e3f8bf373c):
|
||||
|
||||
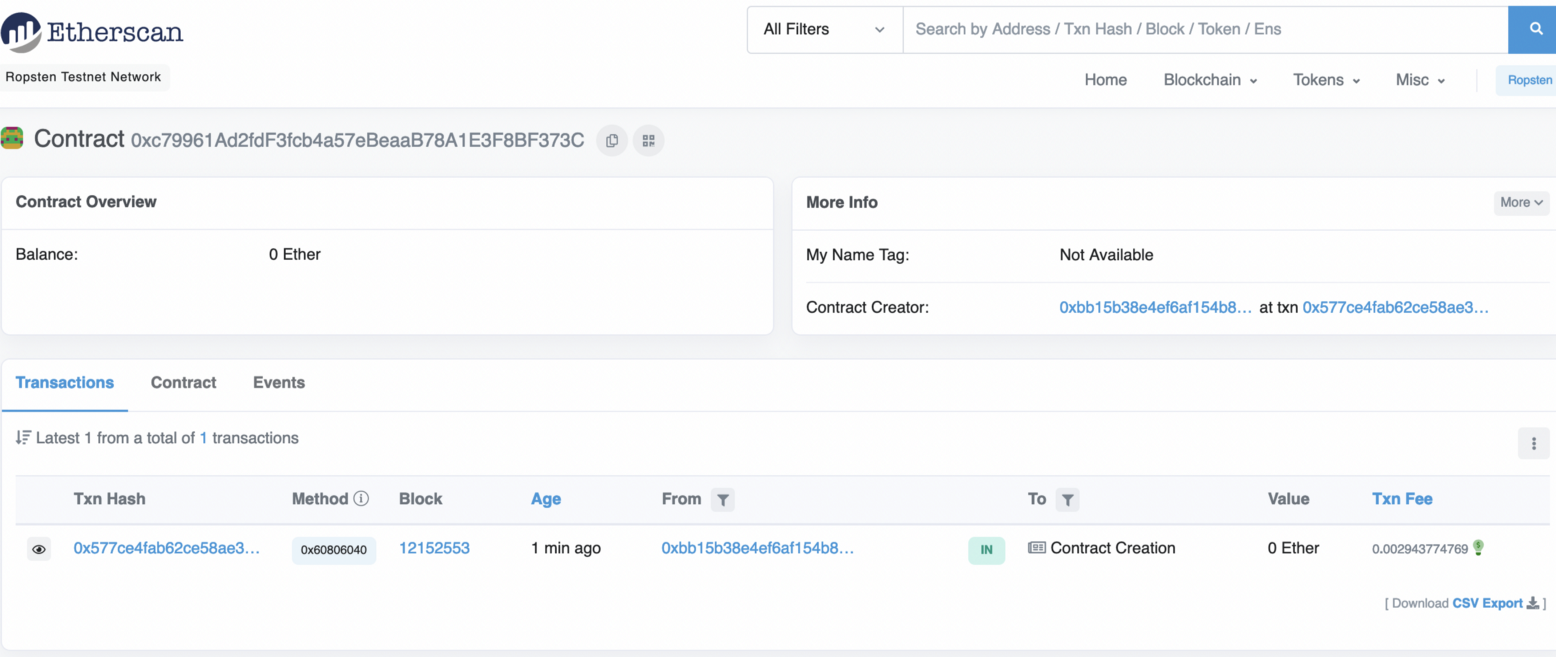
|
||||
|
||||
If we look at the contract we get:
|
||||
|
||||
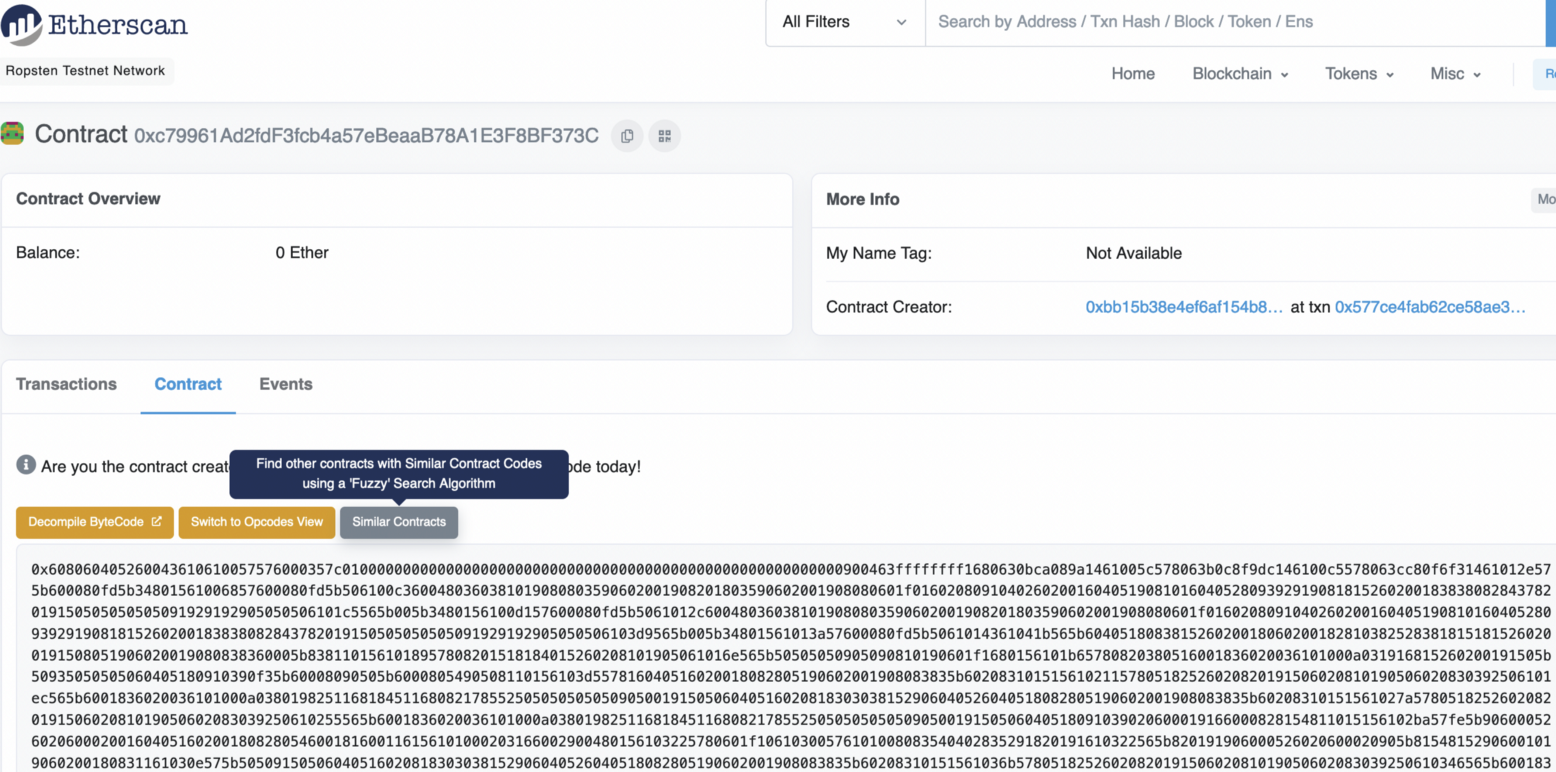
|
||||
|
||||
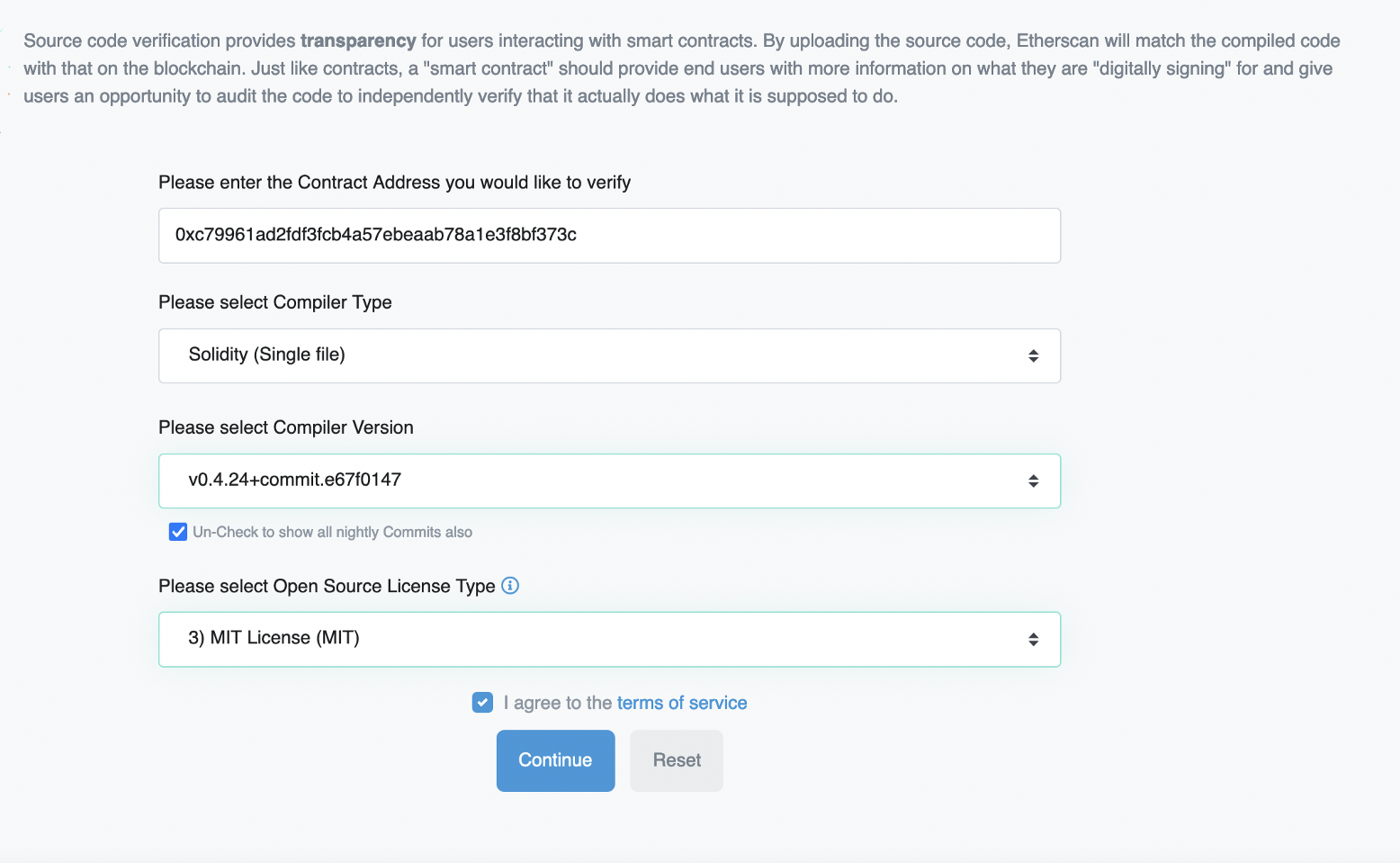
Next we can Verify the contract:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
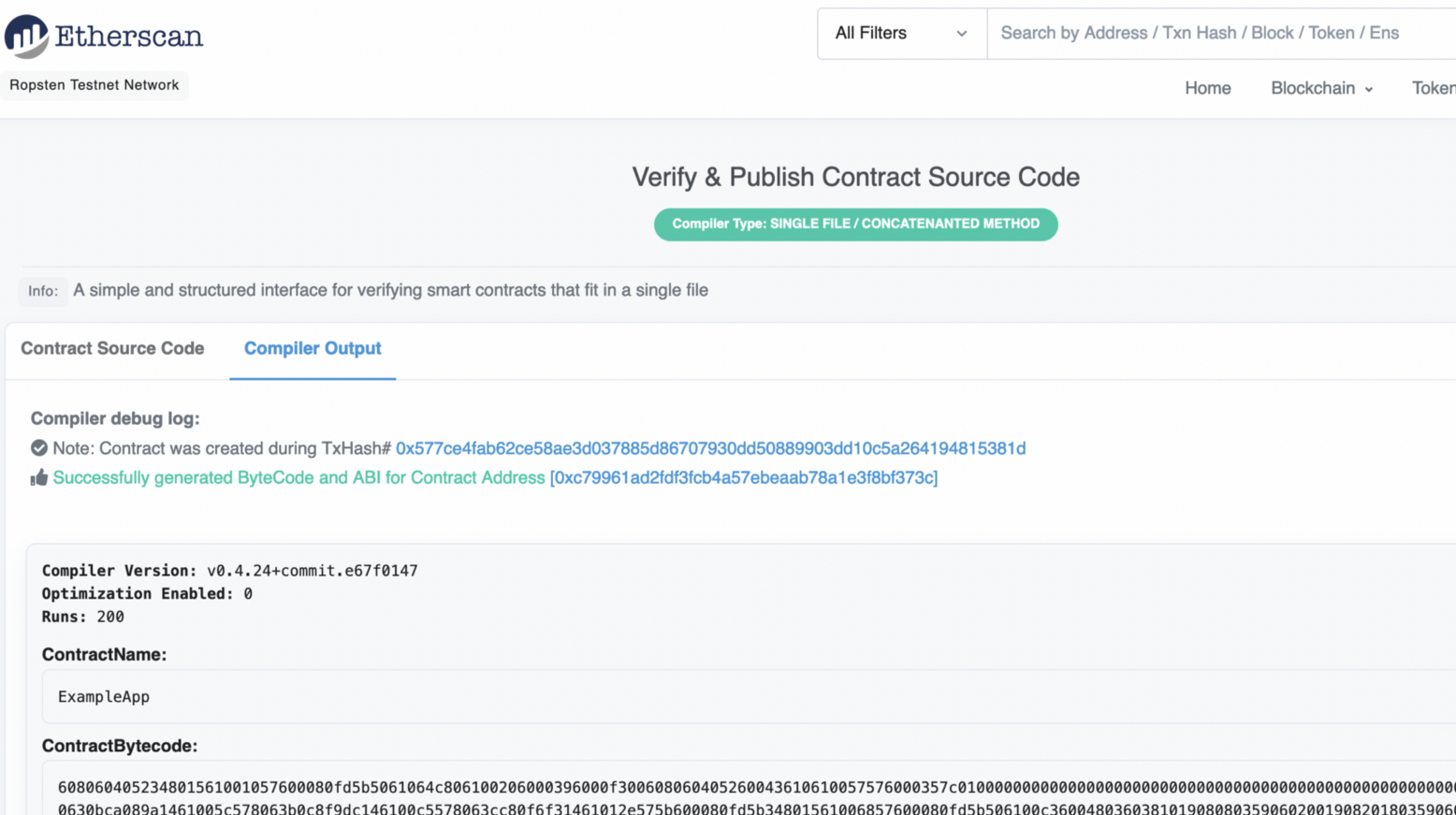
Note that the compiler we used is 0.4.24. We then add our code, and then the contact is validated:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
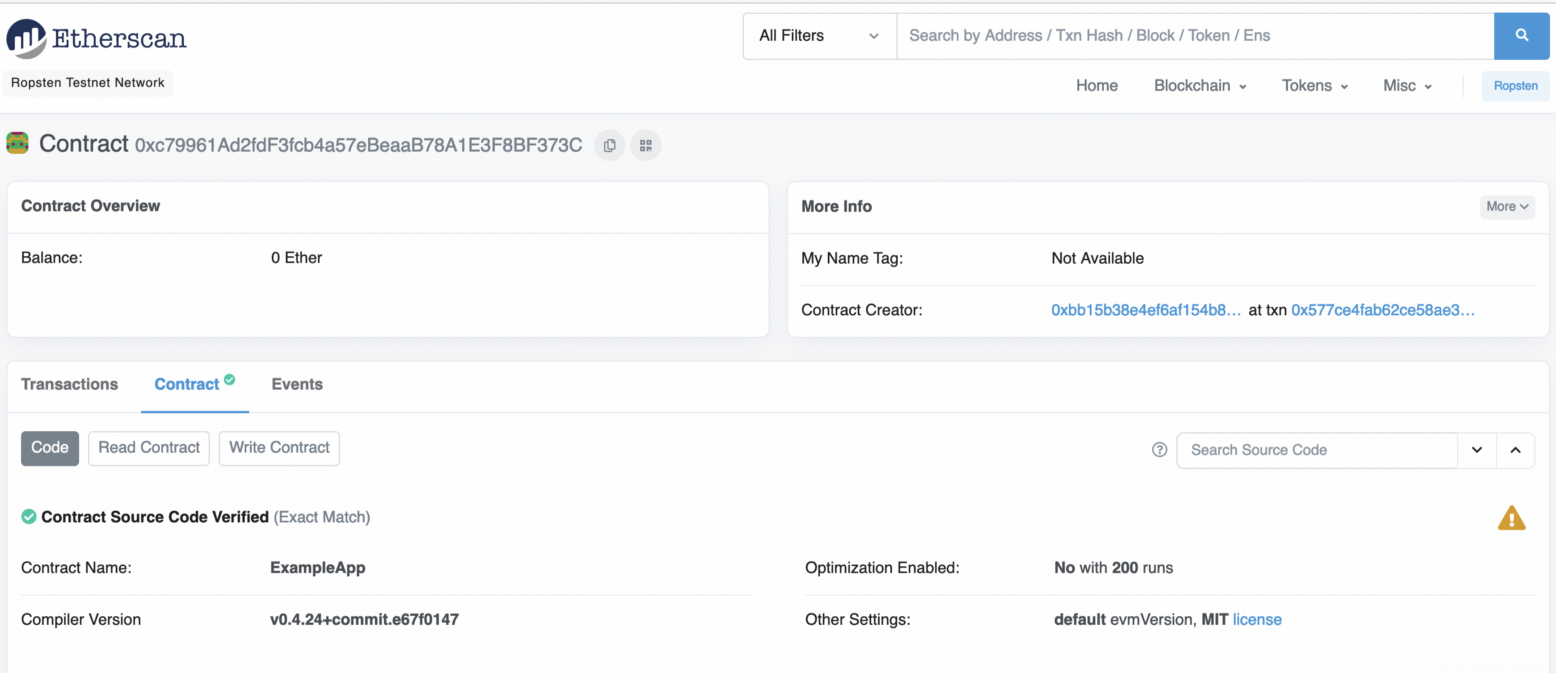
It is now complete [here](https://ropsten.etherscan.io/address/0xc79961ad2fdf3fcb4a57ebeaab78a1e3f8bf373c):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
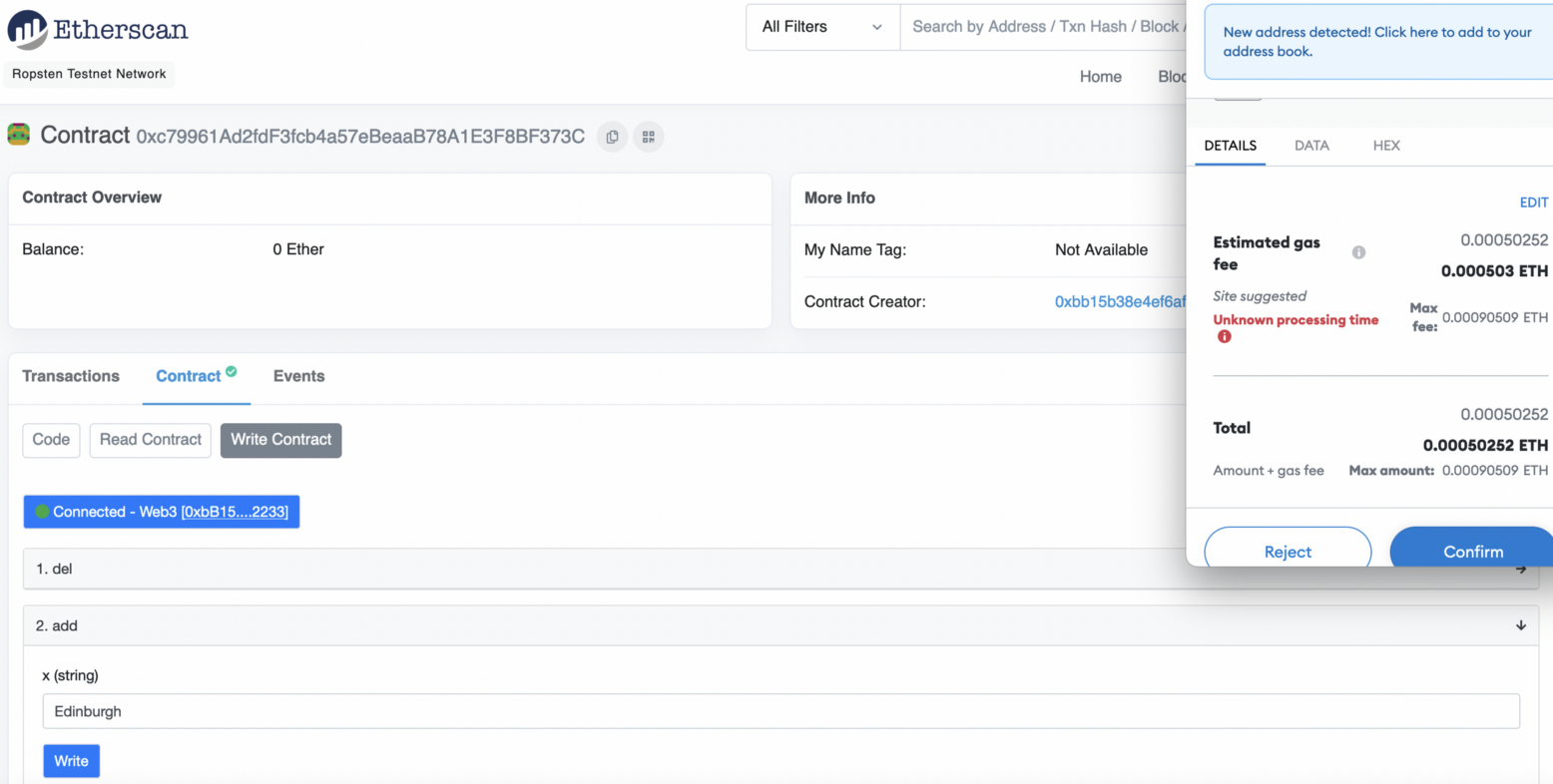
This will cost us some gas as we change the state of the smart contact:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
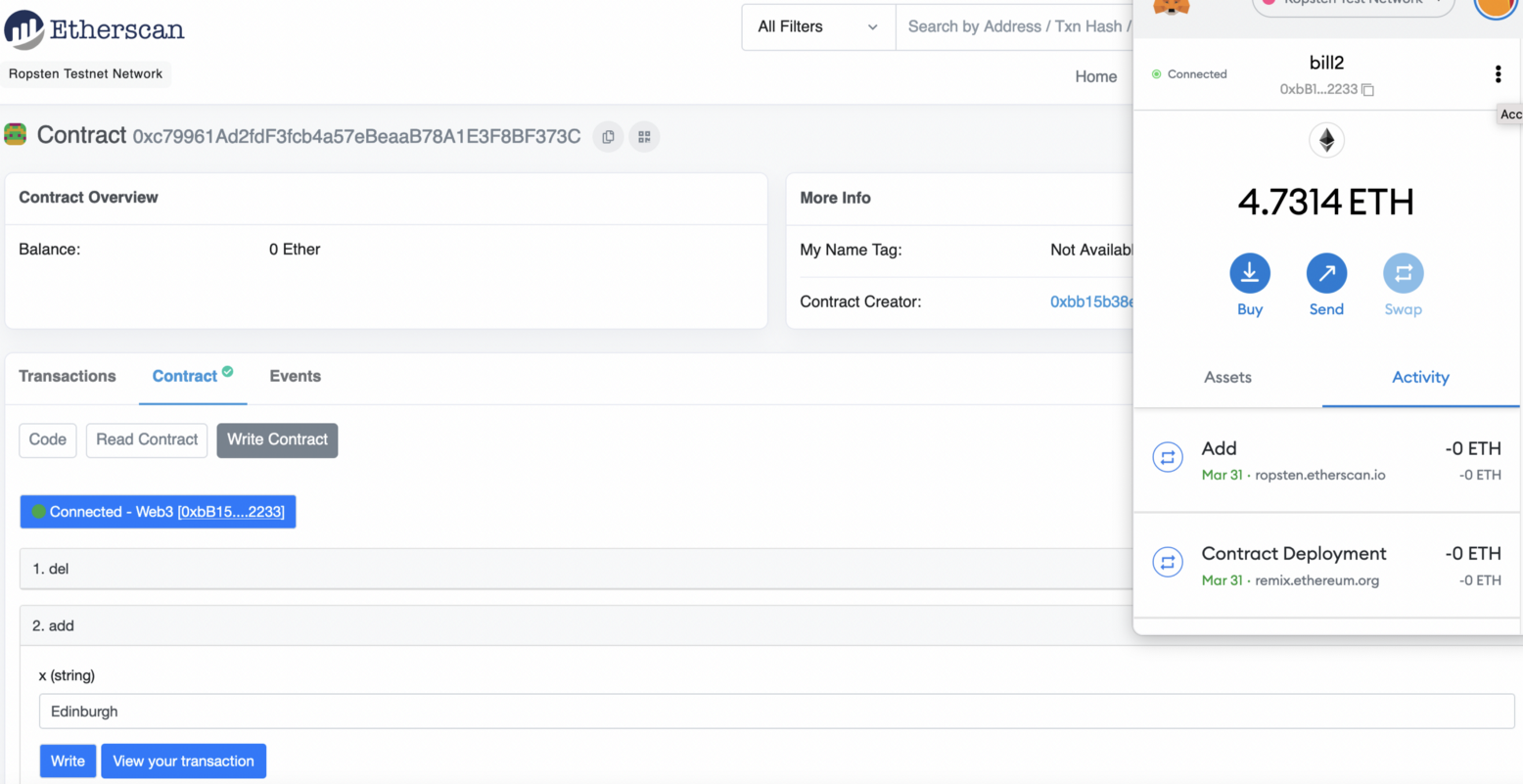
Once it has been mined, the smart contact will be updated:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
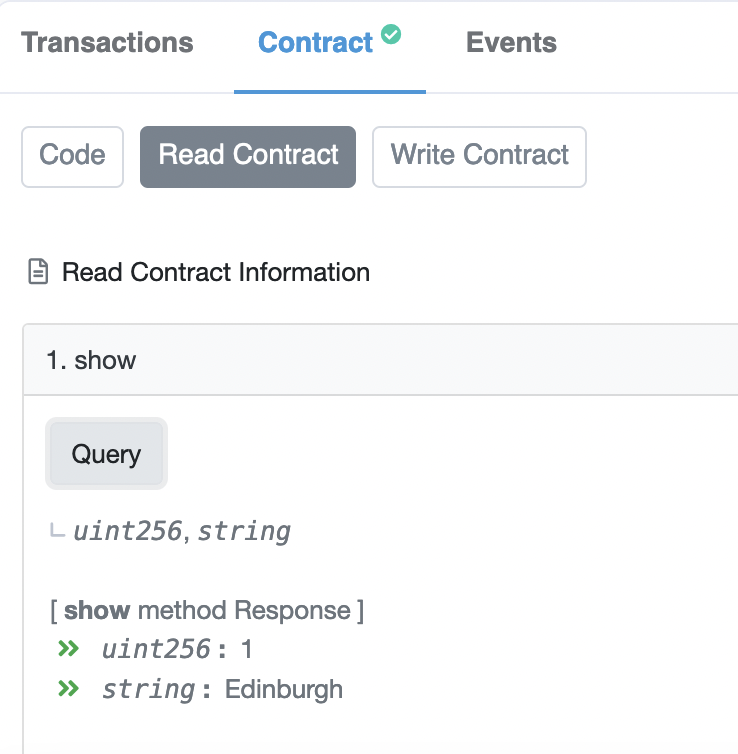
We can then use the View() method to see the string:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
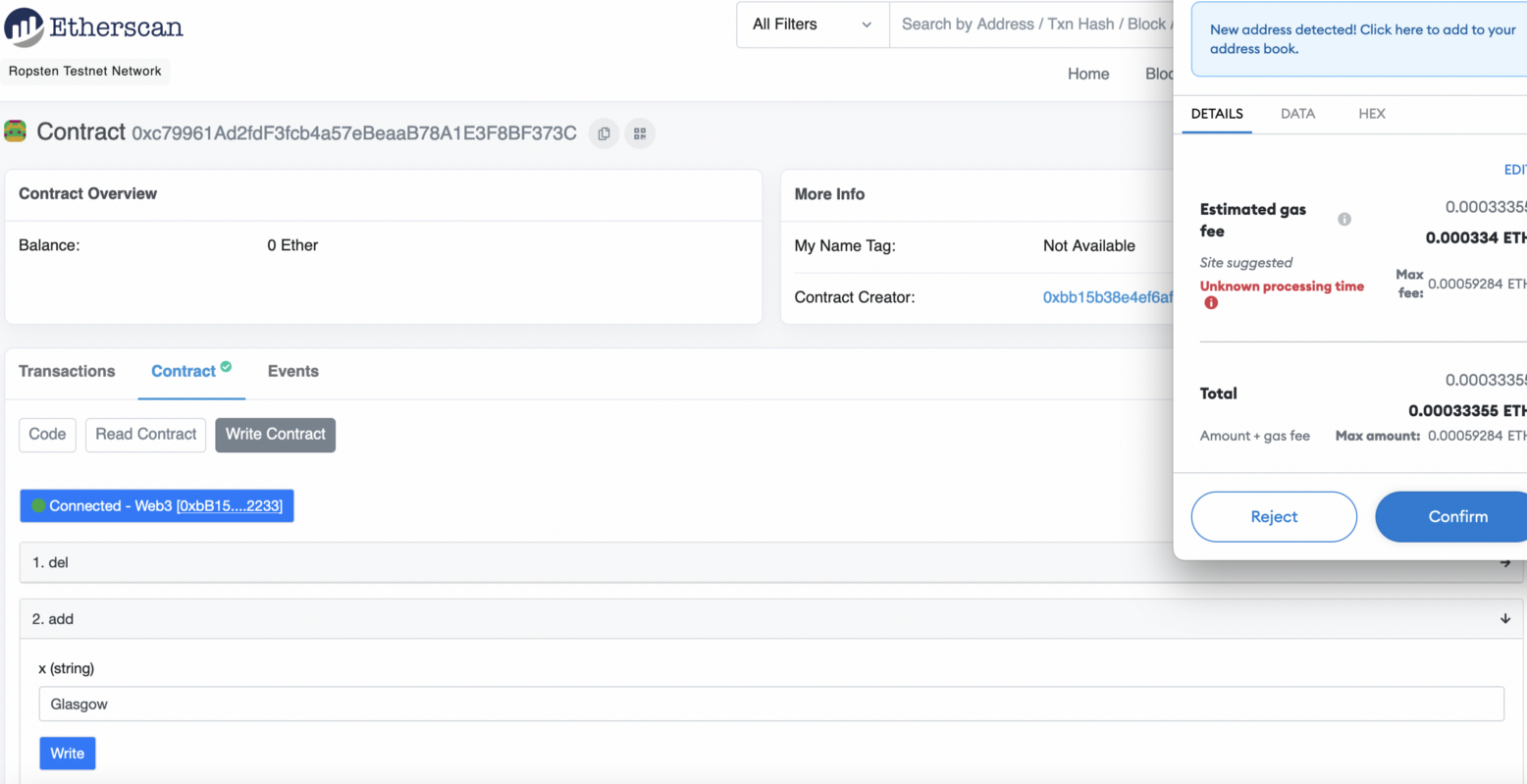
Now we add “Glasgow”:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
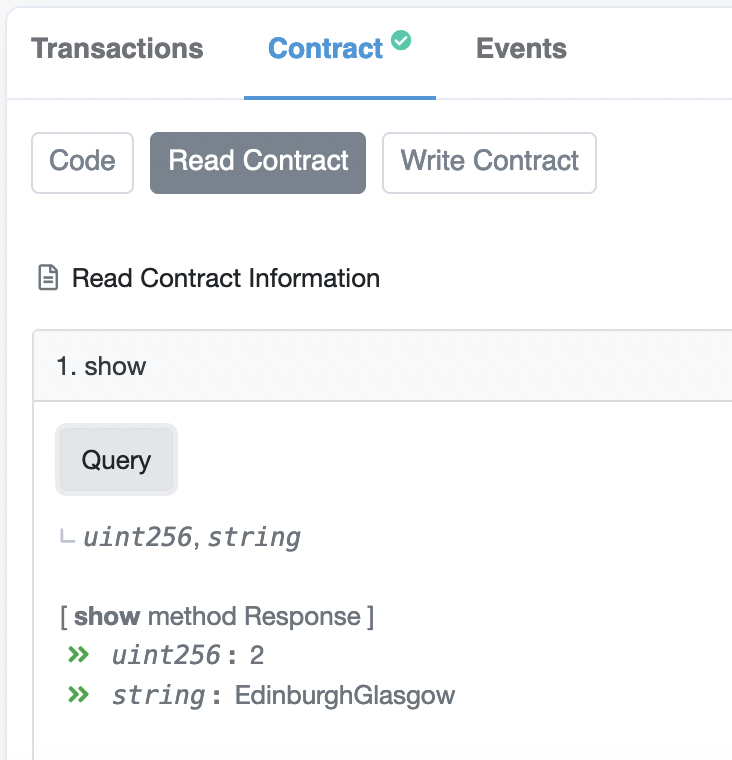
And once it has been mined, we can go back and show the new state:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Complete the following:
|
||||
|
||||
* Setup your smart contact, and then add a few cities of the world, and prove that it works.
|
||||
* Ask another person, or your tutor, to add a city to your smart contract, and prove that it works.
|
||||
|
||||
# Additional Tutorial
|
||||
At the end of this lab, remember to stop your Blockchain (Control-C from the console that is running Geth), and shut down your VM. You may also want to use “rm -r mynapier” in order to delete your blockchain.
|
||||
## Using Geth
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user