mirror of
https://github.com/billbuchanan/appliedcrypto.git
synced 2026-02-20 13:50:42 +00:00
Update README.md
This commit is contained in:
@@ -97,6 +97,94 @@ Once we deploy our contact, we can use Remix to test it. In the following we see
|
||||
|
||||
Test the other functions, and check that they work.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hashing
|
||||
Open Zeppelin is open-source Solidity library that supports a wide range of functions that integrate into smart contracts in Ethereum. In the following we will implement a number of standard hashing methods, alongside a Base64 integration from Open Zeppelin:
|
||||
|
||||
```Solidity
|
||||
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
|
||||
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Base64.sol";
|
||||
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Strings.sol";
|
||||
|
||||
contract Hashit {
|
||||
|
||||
function getKeccak256(string memory str) public pure returns(bytes32){
|
||||
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked(str));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getSha256(string memory str) public pure returns (bytes32) {
|
||||
return sha256(abi.encodePacked(str));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getBase64(string memory str) public pure returns(string memory){
|
||||
return Base64.encode(abi.encodePacked(str));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getStringHex(uint256 str) public pure returns(string memory){
|
||||
return Strings.toHexString(str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getString(uint256 str) public pure returns(string memory){
|
||||
return Strings.toString(str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With this, we get a number of solidity code integrations that enhance smart contracts:
|
||||
|
||||
The integration is fairly simple, and where we just pick the required solidity file integration (after reviewing it, of course). In the following we integrate with Base64 and Strings:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Base64.sol";
|
||||
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Strings.sol";
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are certain standard hash functions that integrate into Solidity. These include keccak256() and sha256():
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
function getKeccak256(string memory str) public pure returns(bytes32){
|
||||
return keccak256(abi.encodePacked(str));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
function getSha256(string memory str) public pure returns (bytes32) {
|
||||
return sha256(abi.encodePacked(str));
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can then create our smart contract in Remix [here], and compile the contract:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
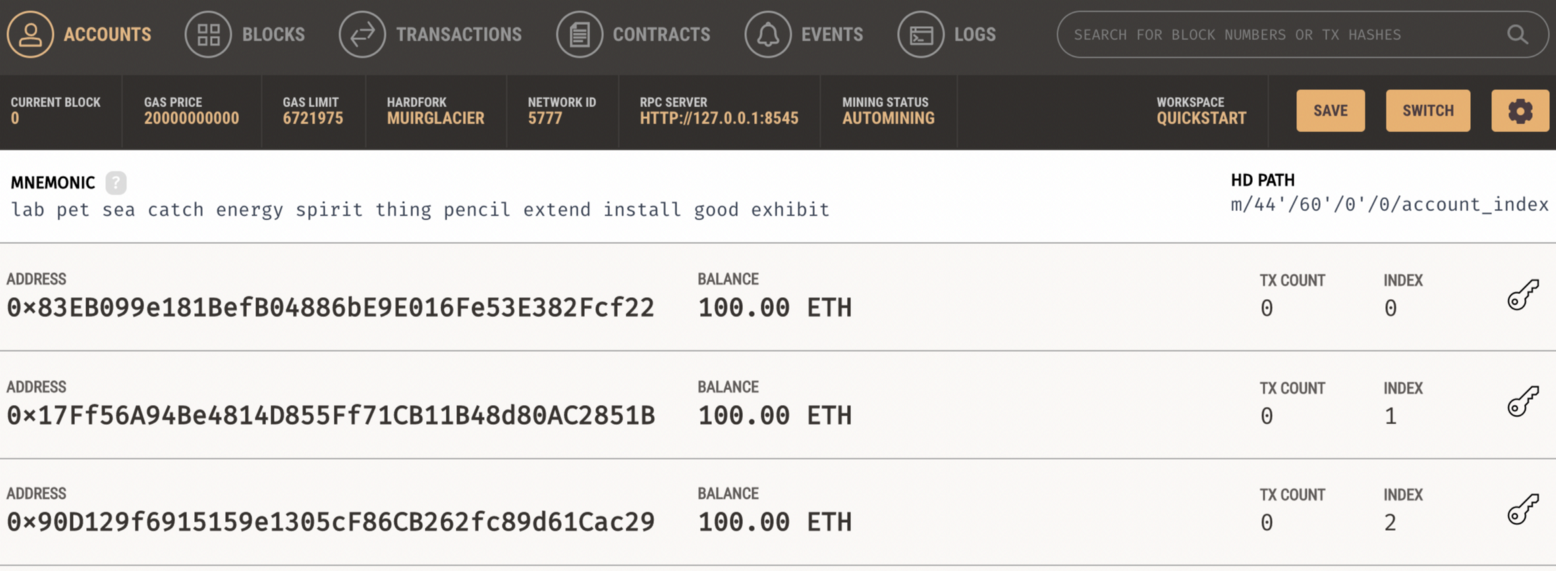
Now we can start our local blockchain with Ganache:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
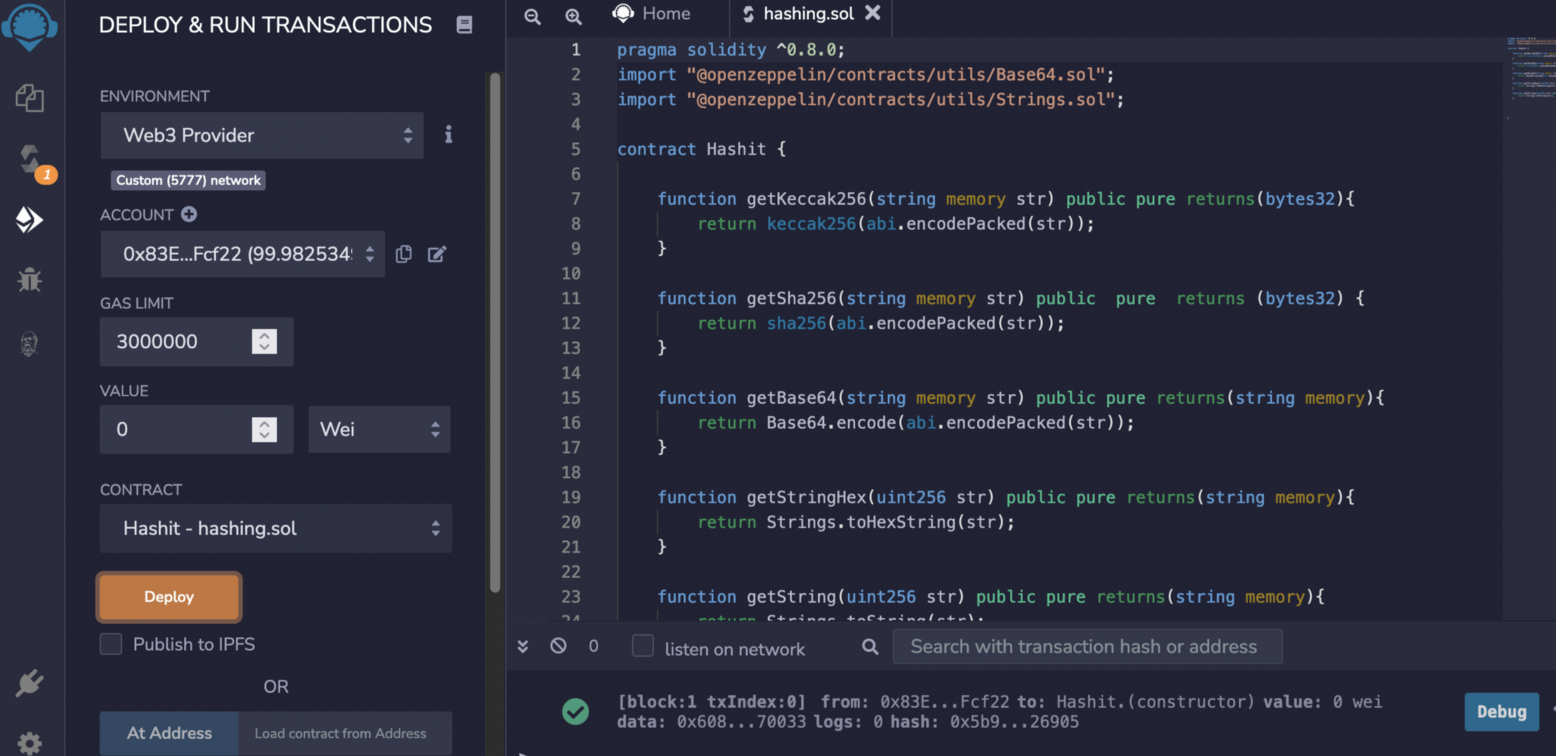
And then deploy our smart contact:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
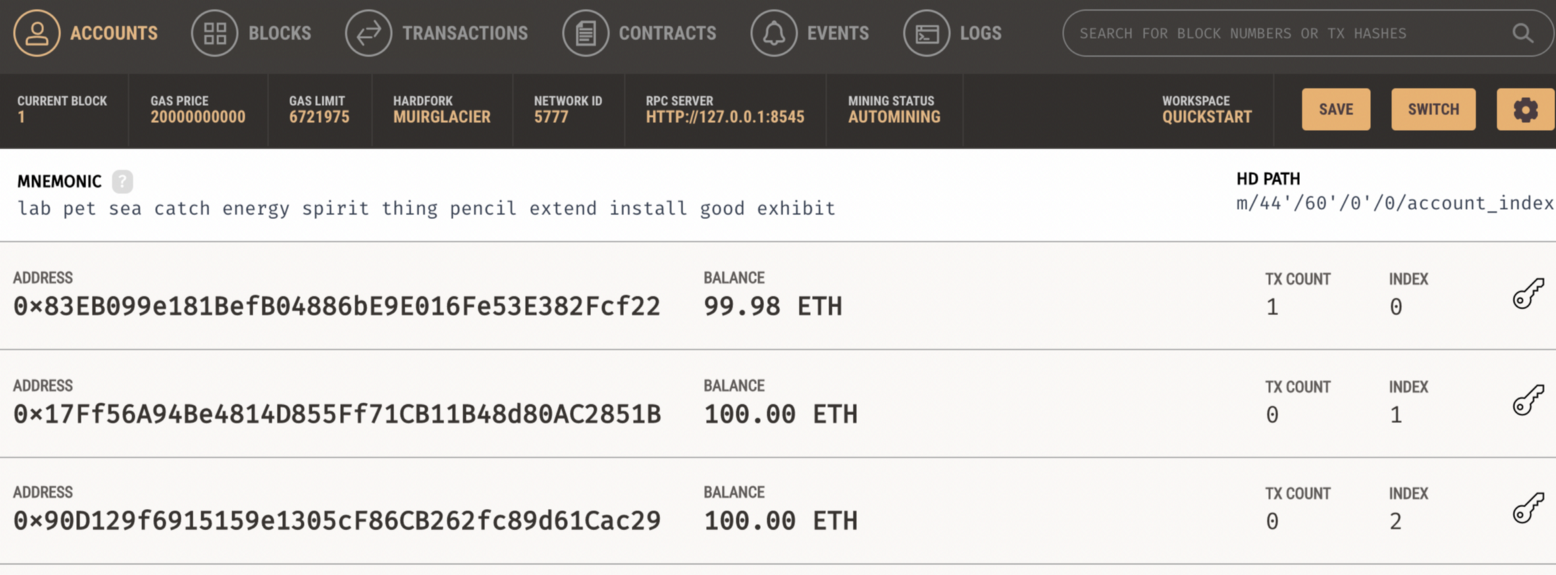
We then see that this has cost one of the accounts some amount of gas:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
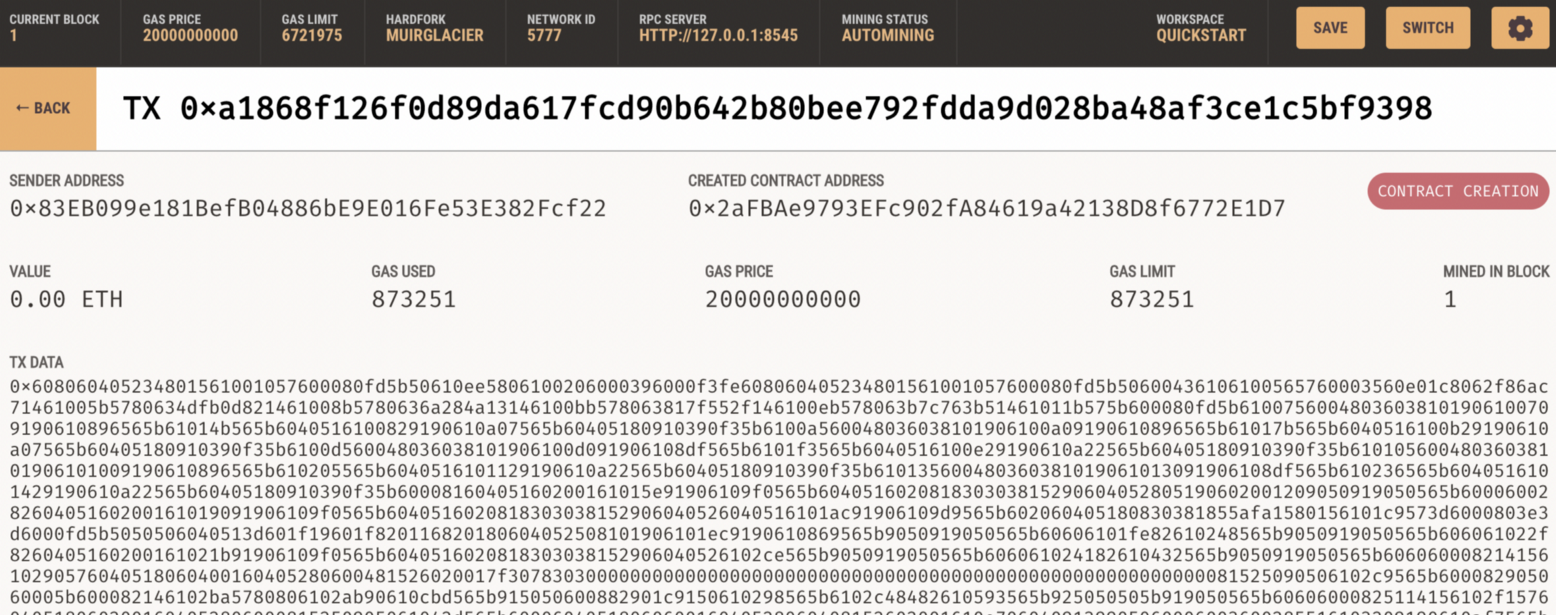
And then we see we have a contract:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
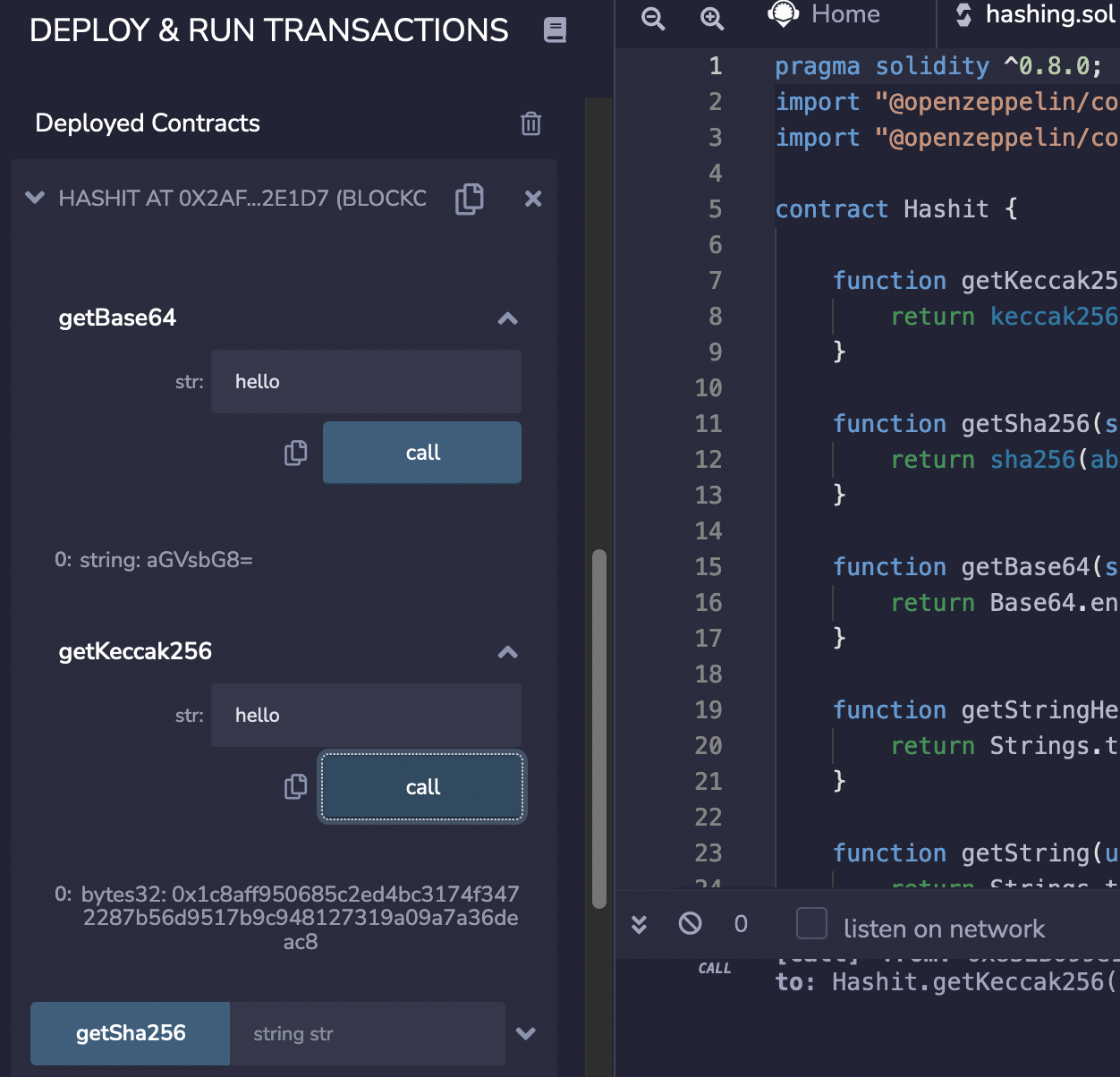
Now we can go ahead and test the contract:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In this case we see that the Base64 string for “hello” is “aGVsbG8=”, and that the Keccak-256 hash for “hello” is “0x1c8aff950685c2ed4bc3174f3472287b56d9517b9c948127319a09a7a36deac8”. You can test this [here]:
|
||||
|
||||
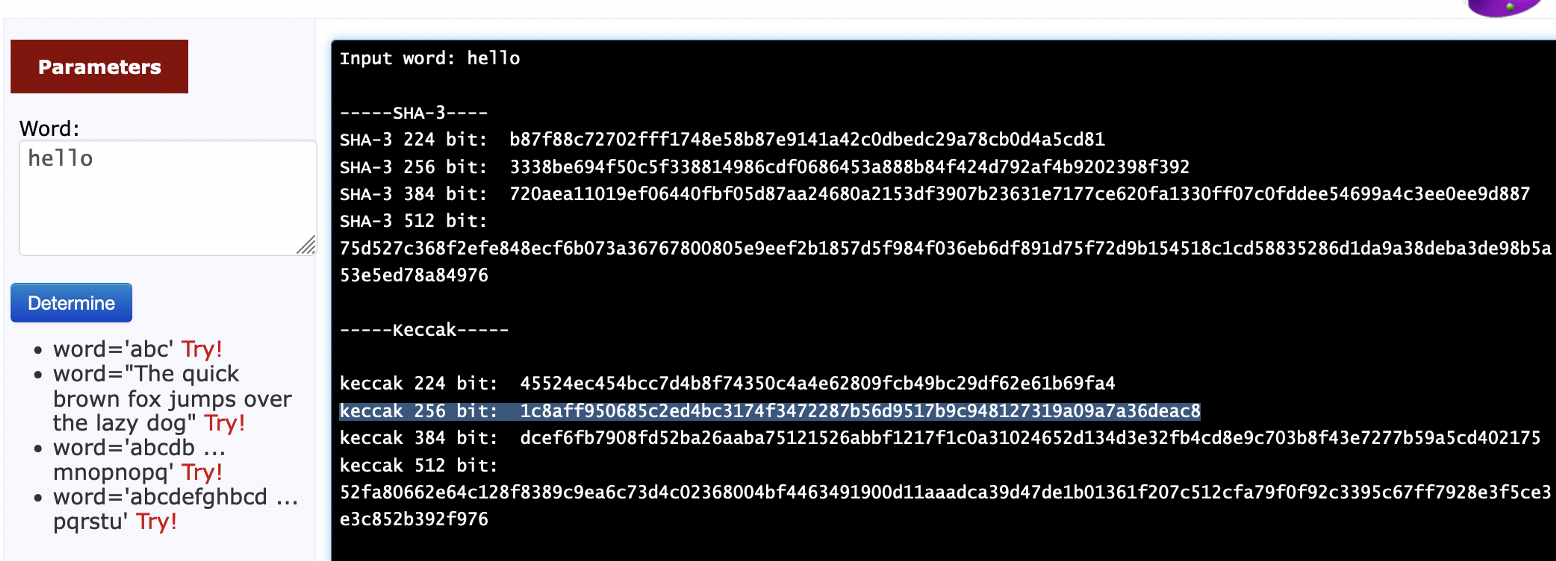
|
||||
|
||||
And [here] for Base64:
|
||||
|
||||
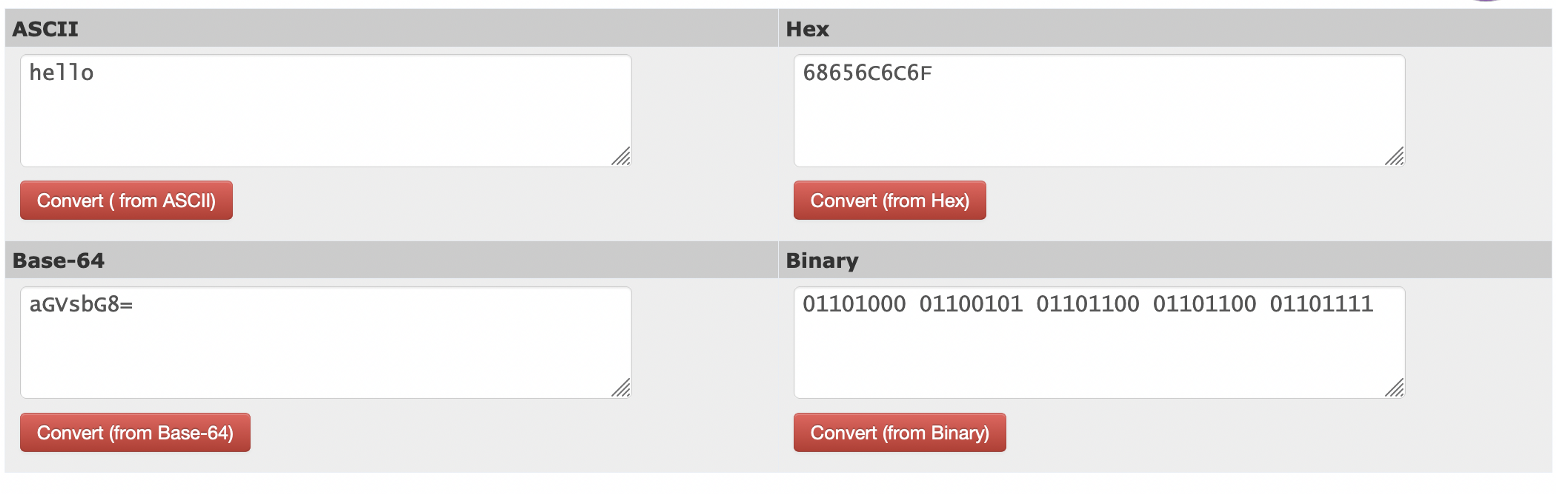
|
||||
|
||||
Now go ahead and test each of the methods, and prove that they work.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Light-weight crypto
|
||||
### L1
|
||||
In many operations within public key methods we use the exponential operation:
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user